Counselling
Counselling psychology as a psychological specialty facilitates personal and interpersonal functioning across the life span with a focus on emotional, social, vocational, educational, health-related, developmental, and organizational concerns. Through the integration of theory, research, and practice, and with sensitivity to multicultural issues, this specialty encompasses a broad range of practices that help people improve their well-being, alleviate distress and maladjustment, resolve crises, and increase their ability to live more highly functioning lives. Counseling psychology is unique in its attention both to normal developmental issues and to problems associated with physical, emotional, and mental disorders.
Clinical psychology is a branch of psychology devoted to understanding mental health problems in individuals and developing effective treatments for the full spectrum of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders one may experience; depression, anxiety disorders, interpersonal difficulties, and psychotic disorders are but a few. Clinical psychologists are service providers, many of whom work in clinical settings while others choose academic careers or careers in Consulting. As a group, clinical psychologists are skilled in clinical practice as well as research on clinical problems and clinical interventions.
What is the difference between counselling and clinical psychology?

Traditionally, the main difference between counseling and clinical psychology is their perspective and training. Counseling psychologists focus more on the psychologically healthy individual where clinical focuses on individuals with serious mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia). Counseling psychology has grown out of vocational psychology and has a strong educational component. CP programs are also typically housed in a school of education (though not all of them are). Clinical programs are more medically orientated in nature focusing on treatment of disease, in this case mental illness.
Counselling psychologists are considered to be the generalists, they are trained in a wide variety of basic therapeutic skills. Clinical psychologists are typically focused in one or a few areas (e.g. depression, substance abuse). Counseling psychologists can and do specialize, but their training is focused on a general repertoire of skills. Counseling and clinical psychologists can generally treat the same kind of patients and the overlap between the two fields continues to grow.
Counselling relationship
 The relationship between a counselor and client is the feelings and attitudes that a client and therapist have towards one another, and the manner in which those feelings and attitudes are expressed. The relationship may be thought of in three parts: transference/counter transference, working alliance, and the real- or personal-relationship.
Transference can be described as the client’s distorted perceptions of the therapist. This can have a great affect on the therapeutic relationship. For instance, the therapist may have a facial feature that reminds the client of their parent. Because of this association, if the client has significant negative/positive feelings toward their parent, they may project these feelings onto the therapist. This can affect the therapeutic relationship in a few ways. For example, if the client has a very strong bond with their parent, they may see the therapist as a father/mother figure and have a strong connection with their therapist. This can be problematic because as a therapist, it is not ethical to have a more than “professional” relationship with a client. It can also be a good thing, because the client may open up greatly to the therapist. In another way, if the client has a very negative relationship with their parent, the client may feel negative feelings toward the therapist. This can then affect the therapeutic relationship as well. For example, the client may have trouble opening up to the therapist because he/she lacks trust in their parent (projecting these feelings of distrust onto the therapist).
The relationship between a counselor and client is the feelings and attitudes that a client and therapist have towards one another, and the manner in which those feelings and attitudes are expressed. The relationship may be thought of in three parts: transference/counter transference, working alliance, and the real- or personal-relationship.
Transference can be described as the client’s distorted perceptions of the therapist. This can have a great affect on the therapeutic relationship. For instance, the therapist may have a facial feature that reminds the client of their parent. Because of this association, if the client has significant negative/positive feelings toward their parent, they may project these feelings onto the therapist. This can affect the therapeutic relationship in a few ways. For example, if the client has a very strong bond with their parent, they may see the therapist as a father/mother figure and have a strong connection with their therapist. This can be problematic because as a therapist, it is not ethical to have a more than “professional” relationship with a client. It can also be a good thing, because the client may open up greatly to the therapist. In another way, if the client has a very negative relationship with their parent, the client may feel negative feelings toward the therapist. This can then affect the therapeutic relationship as well. For example, the client may have trouble opening up to the therapist because he/she lacks trust in their parent (projecting these feelings of distrust onto the therapist).
Another theory about the function of the counseling relationship is known as the secure-base hypothesis, which is related to attachment theory.
This hypothesis proposes that the counselor acts as a secure-base from which clients can explore and then check in with. Secure attachment to
one’s counselor and secure attachment in general have been found to be related to client exploration. Insecure attachment styles have been found
to be related to less session depth than securely attached client.
Counselling Ethics

Perceptions on ethical behaviors vary depending upon geographical location. Although, ethical mandates are similar throughout our global community. The standard ethical behaviors are centered on “doing no harm” and preventing harm. As counselors, it is standard that a counselor should take appropriate action to prevent harm.
Ethical standards are similar in that you should shall not share information that is obtained through the counseling process without specific written consent by the client or legal guardian except to prevent clear, imminent danger to the client or others or when required to do so by a court order.
Counselors are held to a higher standard that most professionals because of the intimacy of their therapeutic delivery. Counselors are not only to avoid fraternizing with their clients. They should avoid dual relationships, and never engage in sexual relationships.
Ethical standards are created to help practitioners, clients and the community avoids any possible harm or potential for harm. Ethical standards are a guideline, but for specific standards they are mandates. Recognizing the differences is clear in a majority of organizational codes of ethics.
In the 21st century the main disease suggested is the stress. Now everything blood pressure, depressive illnesses as diabetes accounts for this. Normal life took a very nasty disturbed swing during stress along with the stress to the diseases. As on today people at the age of 5 to 20, are especially in high stress and suffering. All over the world the statistics are the following: 69% of people in the world affected by mental stress.
76% of people have not had enough sleep.
77% of people mental stresses in family relations have been afraid.
50% of people do not accept new a material is a major concern.
55% people are having less friends circle.
58% of the peoples are affected by headache.
70% of people are right to be angry.
Adds more stress a person’s biological age as 30 years, according to recent research.
What causes stress?
Stress can come in two types. One is activity of the social surrounding of us and another one is our lifestyle. Disappointment, fear, rejection, inflammation, more work, more effort, confusion, some of these factors can cause stress. Some more light, stress caused by factors such as too much noise.
Birth, death, wars, marriages, divorce, illness, job loss, name loss, debt, poverty, selection, traffic congestion, work stress,
anger, relationship breakdown, relationship troubles, as all around us takes all factors of mental pressure on us.
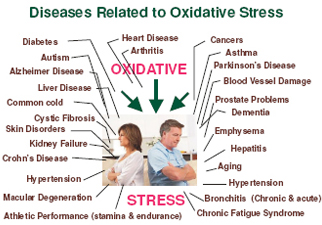
Stress caused by bad habits?
Smoking, lack of proper food habits, medical drug habits, alcoholism, lack of proper sleep, we purchased all of the stress. Nikkottin to stone when smoked in the body for energy research has been proven to increase stress.
If you follow something in the below then we can able to reduce our Mental stress and be free in our life.
Opposition to test it to your clothes!
If you hate the place you check it!
It is sad if test your skills!
If poverty is to test your honesty!
If FICKLENESS Endurance test for you!
If it fails the test of your strength!
If I test your patience!
If it is idle to active test you!
Such a champion across the speed break
Wisdom the ladder to generate the successful!
For more details Visit
http://www.tn.gov.in/service/dept/11
http://india.gov.in/ministry-health-and-family-welfare-6
